Service Resiliency
|
Before Start
You should have NO virtualservice nor destinationrule (in |
Retry
Instead of failing immediately, retry the Service N more times
We will make pod recommendation-v2 fail 100% of the time. Get one of the pod names from your system and replace on the following command accordingly:
kubectl exec -it -n tutorial $(kubectl get pods -n tutorial|grep recommendation-v2|awk '{ print $1 }'|head -1) -c recommendation /bin/bashYou will be inside the application container of your pod recommendation-v2-2036617847-spdrb. Now execute:
curl localhost:8080/misbehave
exitThis is a special endpoint that will make our application return only `503`s.
You will see it works every time because Istio will retry the recommendation service automatically and it will land on v1 only.
./scripts/run.sh
customer => preference => recommendation v1 from '2036617847-m9glz': 196
customer => preference => recommendation v1 from '2036617847-m9glz': 197
customer => preference => recommendation v1 from '2036617847-m9glz': 198If you open Kiali, you will notice that v2 receives requests, but that failing request is never returned to the user as preference will retry to establish the connection with recommendation, and v1 will reply.
kubectl -n istio-system port-forward $(kubectl -n istio-system get pod -l app=kiali -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}') 20001:20001
open http://localhost:20001/consoleIn Kiali, go to Graph, select the recommendation square, and place the mouse over the red sign, like the picture bellow.
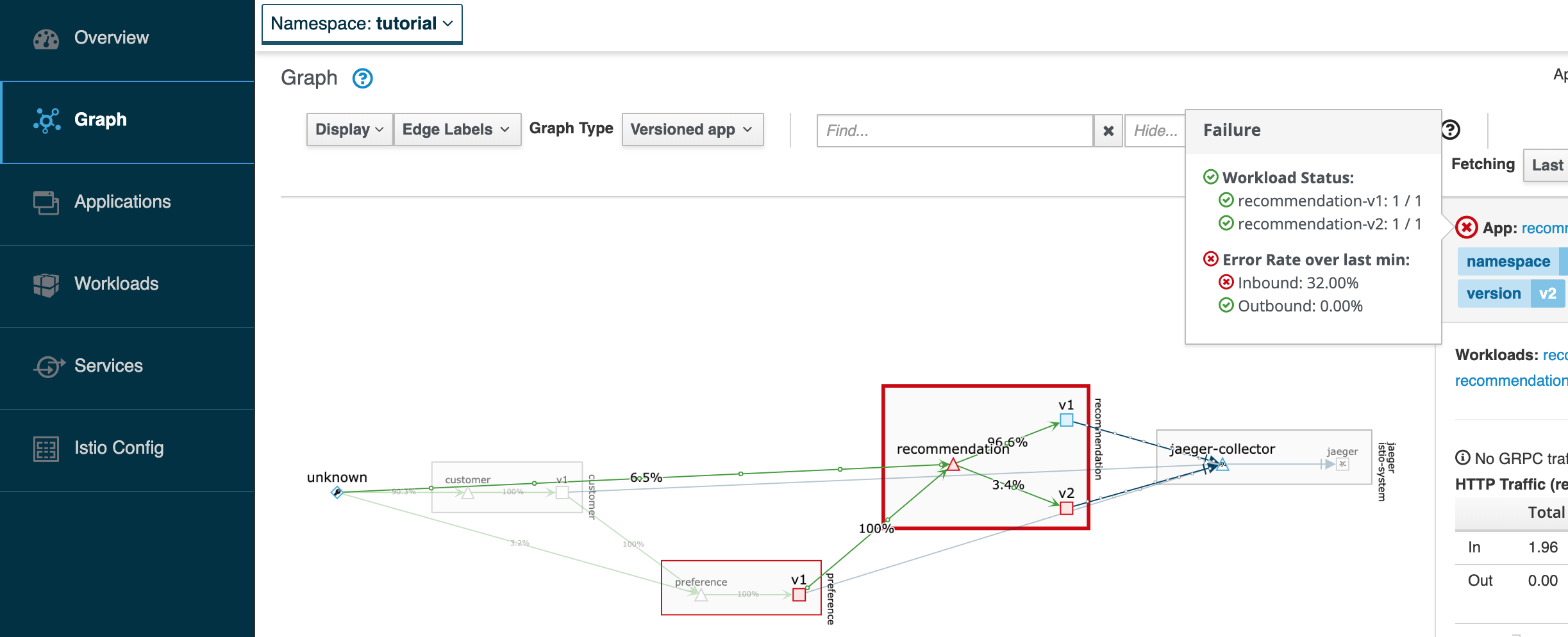
Now, make the pod v2 behave well again
kubectl exec -it -n tutorial $(kubectl get pods -n tutorial|grep recommendation-v2|awk '{ print $1 }'|head -1) -c recommendation /bin/bashYou will be inside the application container of your pod recommendation-v2-2036617847-spdrb. Now execute:
curl localhost:8080/behave
exitThe application is back to random load-balancing between v1 and v2
./scripts/run.sh
customer => preference => recommendation v1 from '2039379827-h58vw': 129
customer => preference => recommendation v2 from '2036617847-m9glz': 207
customer => preference => recommendation v1 from '2039379827-h58vw': 130Timeout
Wait only N seconds before giving up and failing. At this point, no other virtual service nor destination rule (in tutorial namespace) should be in effect. To check it run kubectl get virtualservice kubectl get destinationrule and if so kubectl delete virtualservice virtualservicename -n tutorial and kubectl delete destinationrule destinationrulename -n tutorial
| You will deploy docker images that were privously built. If you want to build recommendation to add a timeout visit: Modify recommendation:v2 to have timeout |
First, introduce some wait time in recommendation v2 by making it a slow performer with a 3 second delay by running the command
kubectl patch deployment recommendation-v2 -p '{"spec":{"template":{"spec":{"containers":[{"name":"recommendation", "image":"quay.io/rhdevelopers/istio-tutorial-recommendation:v2-timeout"}]}}}}' -n tutorialHit the customer endpoint a few times, to see the load-balancing between v1 and v2 but with v2 taking a bit of time to respond
./scripts/run.shThen add the timeout rule
kubectl create -f istiofiles/virtual-service-recommendation-timeout.yml -n tutorialYou will see it return v1 after waiting about 1 second. You don’t see v2 anymore, because the response from v2 expires after the timeout period and it is never returned.
./scripts/run.sh http://istio-ingressgateway-istio-system.$(minishift ip).nip.io/customer
customer => preference => recommendation v1 from '6976858b48-cs2rt': 2907
customer => preference => recommendation v1 from '6976858b48-cs2rt': 2908
customer => preference => recommendation v1 from '6976858b48-cs2rt': 2909Clean up
| You will deploy docker images that were privously built. If you want to build recommendation to remove the timeout visit: Modify recommendation:v2 to remove timeout |
Change the implementation of v2 back to the image that responds without the delay of 3 seconds:
kubectl patch deployment recommendation-v2 -p '{"spec":{"template":{"spec":{"containers":[{"name":"recommendation", "image":"quay.io/rhdevelopers/istio-tutorial-recommendation:v2"}]}}}}' -n tutorialThen delete the virtual service created for timeout by:
kubectl delete -f istiofiles/virtual-service-recommendation-timeout.yml -n tutorialor you can run:
./scripts/clean.sh tutorialFail Fast with Max Connections and Max Pending Requests
Load test without circuit breaker
Let’s perform a load test in our system with siege. We’ll have 40 clients sending 1 concurrent requests each:
export INGRESS_PORT=$(kubectl -n istio-system get service istio-ingressgateway -o jsonpath='{.spec.ports[?(@.name=="http2")].nodePort}')
siege -r 40 -c 1 -v $(minikube ip):$INGRESS_PORT/customerYou should see an output similar to this:
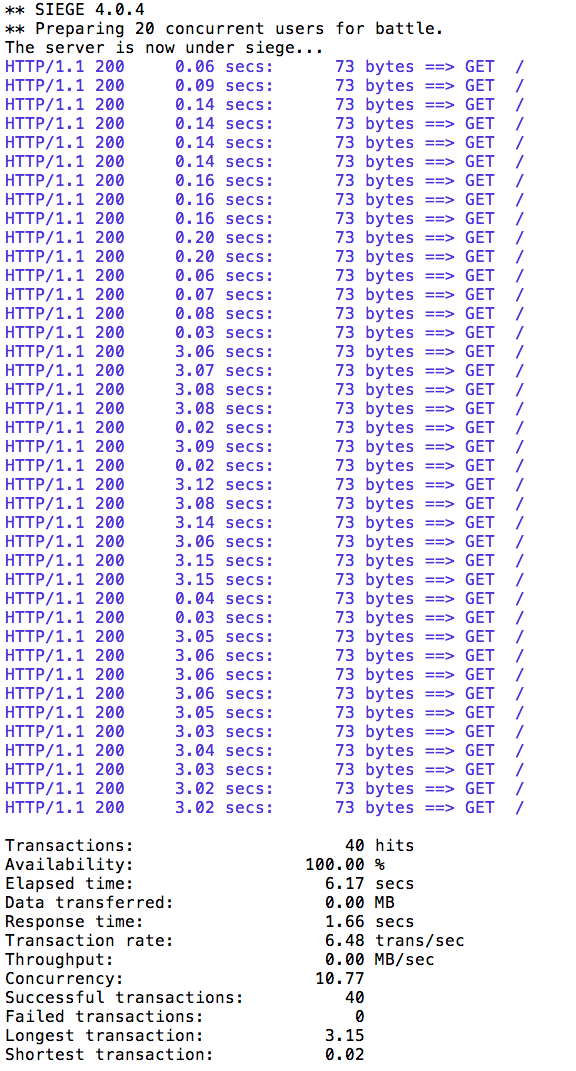
All of the requests to our system were successful.
Load test with circuit breaker
Now let’s see what is the behavior of the system running siege again but having 20 concurrent requests.
export INGRESS_PORT=$(kubectl -n istio-system get service istio-ingressgateway -o jsonpath='{.spec.ports[?(@.name=="http2")].nodePort}')
siege -r 2 -c 20 -v $(minikube ip):$INGRESS_PORT/customer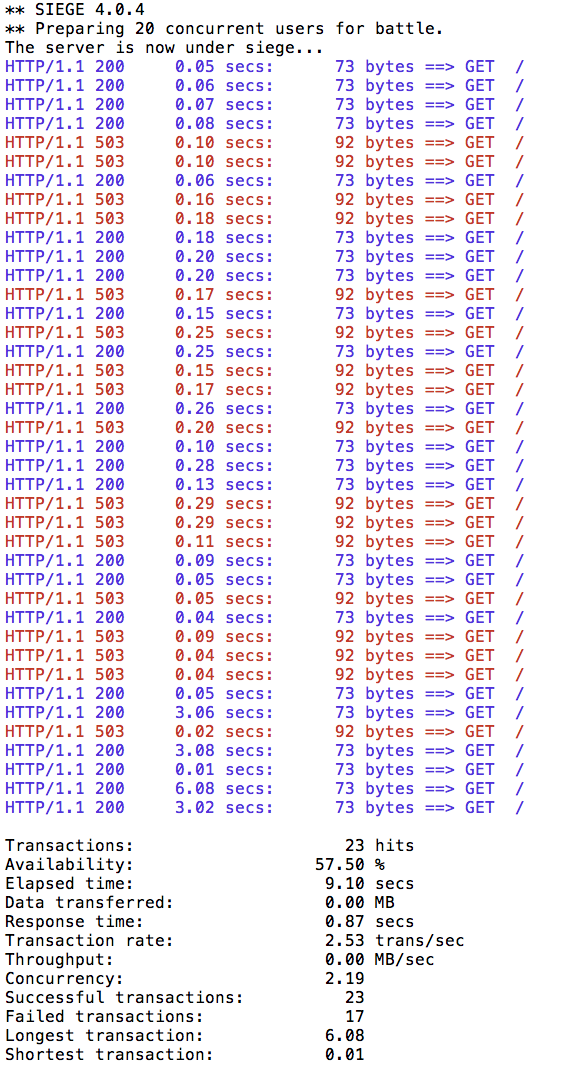
You can run siege multiple times, but in all of the executions you should see some 503 errors being displayed in the results. That’s the circuit breaker being opened whenever Istio detects more than 1 pending request being handled by the instance/pod.